GOOGLE CLOUD PLATFROM ROAD MAP
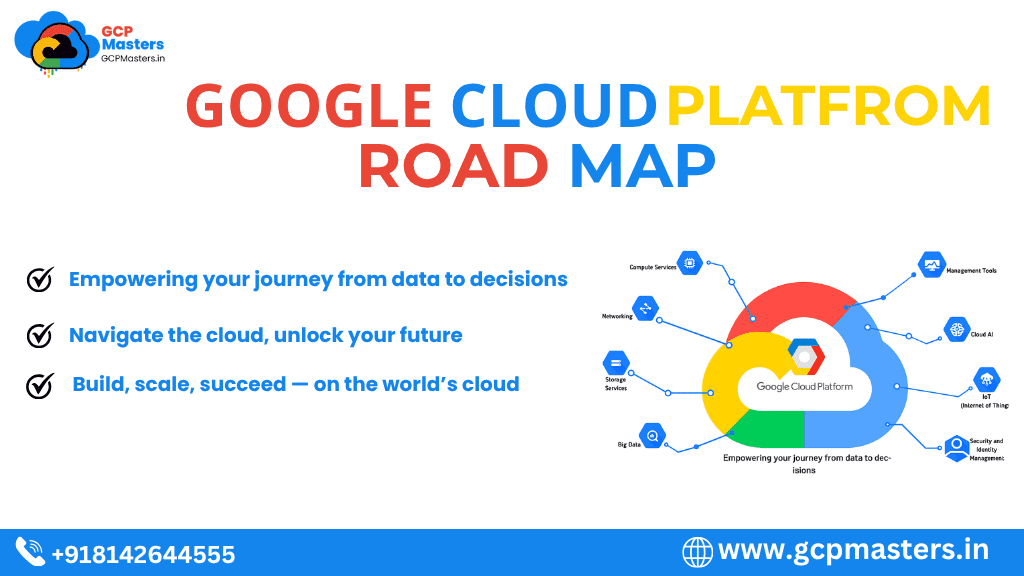
Introduction to GCP Roadmap
What is Google Cloud Platform (GCP)?
- Comprehensive Cloud Ecosystem:
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a collection of cloud computing services provided by Google. It runs on the same secure and reliable infrastructure that powers Google’s internal products such as Search, YouTube, and Gmail. - Wide Range of Services:
GCP offers an extensive set of services covering compute, storage, networking, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. - Core Components:
- Compute Engine for scalable virtual machines
- Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for container orchestration
- App Engine for developing and hosting applications
- BigQuery for high-performance data analytics
- Cloud Storage for secure, scalable object storage
- Vertex AI: Build, Deploy & Scale Machine Learning the Smarter Way
Backup, recovery, - Global Infrastructure:
GCP operates data centres worldwide, ensuring high availability, low latency, and enterprise-grade security. - Use Cases:
- Application development and hosting
- Data processing and analytics
- Machine learning and AI solutions
- Cloud-native DevOps and automation
Why Having a Roadmap Matters (for Businesses and Learners) For Businesses:
- Strategic Planning:
A roadmap helps organizations align their cloud strategy with Google’s future technological direction. - Future-Proofing:
Understanding GCP’s upcoming features enables companies to prepare for new technologies and stay competitive. - Cost Optimization:
Businesses can plan budgets effectively by anticipating service updates, deprecations, and new pricing structures. - Innovation Enablement:
Following the roadmap allows businesses to adopt cutting-edge tools like AI-driven automation and sustainability solutions early. - Risk Management:
Awareness of product lifecycle changes helps mitigate risks related to service migration or compatibility.
For Learners and Cloud Professionals:
- Focused Learning:
The roadmap helps learners identify which technologies and certifications are gaining prominence within the GCP ecosystem. - Career Development:
Staying updated with GCP innovations enhances employability and professional credibility. - Certification Path Planning:
Learners can align study goals with current and upcoming Google Cloud certifications. - Hands-on Experience:
Early exploration of beta or preview services provides practical, real-world learning opportunities. - Community Engagement:
Understanding roadmap trends allows learners to contribute knowledge and insights to professional and open-source communities.
What This Guide Will Cover
1. The Technology Roadmap
- Detailed overview of Google Cloud’s future product and service developments
- Focus areas include:
- Compute and storage innovations
- Data analytics and AI/ML advancements
- Networking, security, and infrastructure updates
- Compute and storage innovations
- Guidance on how to track and interpret the official GCP roadmap
- Practical strategies for businesses to align their operations with upcoming changes

2. The Learning Roadmap
- Structured guide for individuals aiming to build expertise in Google Cloud
- Recommended certification paths for different experience levels
- Resources for hands-on practice and continuous learning
- Tips to keep skills current with Google’s evolving technologies
- Steps to pursue a successful career in cloud computing using GCP
2.1 Compute & InfrastructureEnhancements in Compute Engine and GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine):
- Next-Generation Virtual Machines:
Google is introducing more powerful and efficient VM families designed for specific workloads, including AI training, HPC (High-Performance Computing), and data-intensive applications. - Custom Chip Advancements:
Expansion of TPUs (Tensor Processing Units) and GPUs to accelerate AI workloads while reducing operational costs. - Optimized Performance:
Continuous improvements in startup times, autoscaling capabilities, and resource utilization for both VMs and containers. - Kubernetes Evolution:
- Deeper integration between GKE Autopilot and Cloud Run, simplifying containerized application deployment.
- Better cluster management tools and improved cost visibility.
- Deeper integration between GKE Autopilot and Cloud Run, simplifying containerized application deployment.
- Sustainability Focus:
Compute services are being optimized for energy efficiency, aligning with Google’s goal of operating entirely on carbon-free energy by 2030.
Hybrid and Multicloud: Anthos Expansion
- Broader Platform Support:
Anthos continues to expand compatibility across environments—on-premises, Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure—allowing seamless application management across clouds. - Unified Management Experience:
Enhanced Anthos dashboards now provide consistent policy enforcement, monitoring, and security across hybrid deployments. - Edge Computing Enablement:
Anthos for Edge extends Google Cloud capabilities to edge locations, enabling low-latency processing for IoT and real-time analytics. - Developer Productivity:
Integration with Cloud Build and Cloud Deploy makes CI/CD pipelines easier to implement across multi-cloud setups. - Cost Efficiency:
Multi-cloud cost visibility and workload optimization features are being enhanced to help organizations manage spending across environments
Reliability and Global Network Upgrades
- Expansion of Global Regions and Zones:
Google continues to add new data center regions and availability zones across emerging markets, improving performance and redundancy. - Private Connectivity Upgrades:
New Cloud Interconnect and Private Service Connect updates provide more reliable and secure networking options for enterprise users. - Faster, Smarter Networking:
Enhanced Google Cloud Backbone with better routing efficiency and lower latency for global workloads. - Improved Uptime and SLAs:
Infrastructure upgrades are pushing service-level agreements closer to 99.999% uptime for mission-critical workloads. - Disaster Recovery and Failover:
Advanced regional failover mechanisms and multi-zone replication ensure continuous service availability even during outages. - Security Integration:
Network security enhancements include stronger DDoS protection, encryption in transit, and integration with Google’s Zero Trust framework.
2.2 AI & Machine Learning Vertex AI Future Capabilities
- Unified AI Development Platform:
Google continues to evolve Vertex AI into a single, end-to-end platform for building, deploying, and managing machine learning and generative AI models. - Enhanced Model Management:
New tools will provide better model versioning, experiment tracking, and lifecycle management to simplify MLOps pipelines. - Vertex AI Studio Improvements:
- More intuitive, no-code and low-code interfaces for rapid model prototyping.
- Expanded integration with BigQuery ML and Looker Studio for data-driven AI development.
- Generative AI Tools:
Expansion of Vertex AI Search and Conversation features for developing intelligent chatbots, content generators, and recommendation engines. - Responsible AI Enhancements:
Google is emphasizing fairness, transparency, and compliance by adding built-in tools for bias detection, data lineage, and explainability. - Performance Optimization:
Improved GPU and TPU support will reduce model training costs while enhancing inference speed and scalability.
Gemini AI Models + Enterprise AI Evolution
- Gemini Integration Across GCP:
The Gemini family of AI models (Google’s next-generation large language models) will be more deeply embedded into GCP services, enabling advanced reasoning, coding, and automation capabilities. - AI-Assisted Cloud Management:
Gemini-powered assistants will help cloud administrators automate configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting tasks within GCP. - Enterprise Data Intelligence:
- Seamless integration between Gemini models and BigQuery, Looker, and Vertex AI will allow organizations to derive deeper insights from their data.
- Enterprise-grade fine-tuning options will enable customization for domain-specific use cases.
- Seamless integration between Gemini models and BigQuery, Looker, and Vertex AI will allow organizations to derive deeper insights from their data.
- Multimodal AI Expansion:
Future Gemini updates will support multimodal inputs (text, image, code, and video), enhancing AI-driven creativity and analytics. - Collaboration & Security:
Gemini will provide enterprise-level governance, ensuring data privacy, regulatory compliance, and safe model deployment. - AI Democratization:
Google aims to make AI accessible to all developers and analysts through pre-trained APIs and simplified integration within GCP services.
Agentic and Automated Cloud Operations
- Intelligent Automation with AI Agents:
GCP will introduce AI-driven agents to streamline routine cloud operations such as resource provisioning, cost optimization, and incident response. - Predictive Operations (AIOps):
Leveraging machine learning, Google Cloud will enhance predictive maintenance, automatically detecting and resolving issues before they impact workloads. - Policy-Aware Automation:
Smart agents will enforce organization-wide policies for security, compliance, and resource usage without manual intervention. - Autonomous Infrastructure:
Future updates will bring self-healing infrastructure capabilities that can automatically rebalance workloads and recover from failures. - Operational Insights:
Enhanced observability through Cloud Monitoring and Cloud Logging with AI-based anomaly detection and automated alerts. - Human + AI Collaboration:
Cloud engineers will be able to interact with intelligent assistants that provide actionable insights, configuration recommendations, and remediation options.
2.3 Data Analytics & Storage BigQuery Innovations
- Next-Generation BigQuery Architecture:
Google is enhancing BigQuery to deliver faster query performance, greater scalability, and tighter integration with AI and ML services. - BigQuery Studio Expansion:
- A unified environment for data engineering, analytics, and machine learning within the BigQuery interface.
- Enhanced collaboration features allowing teams to build, test, and deploy analytical models more efficiently.
- Cross-Cloud Querying:
Support for querying data across multiple cloud providers—enabling a truly multicloud analytics experience. - Integration with Vertex AI and Gemini:
Analysts will be able to build and deploy AI-powered insights directly from BigQuery, using natural language prompts and model integration. - Cost Efficiency Enhancements:
Improved auto-scaling, intelligent caching, and tiered storage options to optimize cost-performance balance. - Security and Governance:
Strengthened data classification, access control, and lineage tracking through BigQuery Data Clean Rooms and IAM integration.
Real-Time Analytics Focus
- Streaming Data Enhancements:
Google is improving Dataflow, Pub/Sub, and BigQuery Streaming capabilities to process massive real-time data with lower latency. - Unified Data Pipelines:
Integration between Dataproc, Dataflow, and Datastream will simplify building unified streaming and batch pipelines. - Operational Dashboards:
Real-time visualization capabilities through Looker and Data Studio (Looker Studio) for instant decision-making. - Edge Analytics Enablement:
Real-time processing closer to the data source using Anthos for Edge and Cloud Run for Edge. - Predictive Insights:
AI-enhanced analytics tools will enable predictive modeling directly within real-time data streams, reducing time-to-action. - Event-Driven Architecture:
Support for event-based triggers and serverless functions to automate responses based on live data streams.
Modern Data Architecture Trends
- Data Lakehouse Integration:
Google Cloud is advancing its BigLake framework to unify data lakes and warehouses, providing seamless access to structured and unstructured data. - Unified Metadata Layer:
Enhanced Dataplex for centralized data governance, cataloging, and policy management across distributed data sources. - Composable Data Systems:
Modular, interoperable components allow businesses to mix and match GCP data services based on workload needs. - AI-Driven Data Management:
Incorporation of machine learning for intelligent data lifecycle management, schema optimization, and anomaly detection. - Data Mesh Architecture Support:
GCP tools will continue evolving to support decentralized data ownership models, empowering domain-specific teams.
- Data Lakehouse Integration:
- Sustainability and Cost Transparency:
Tools like Carbon Footprint Dashboard and Cloud Billing Reports will provide visibility into data workloads’ environmental and financial impact.

2.4 Security & Governance Zero Trust Improvements
- Expansion of BeyondCorp Enterprise:
Google is strengthening its Zero Trust architecture through expanded BeyondCorp capabilities, allowing secure, identity-aware access to applications and services—without relying on traditional VPNs. - Context-Aware Access Controls:
Policies will increasingly factor in user identity, device posture, location, and behavior to grant or deny access dynamically. - Deeper Integration with Cloud Services:
Zero Trust security principles are being extended to Compute Engine, GKE, Cloud Storage, and BigQuery for consistent enforcement. - Adaptive Threat Detection:
AI-powered monitoring tools will identify anomalies in user behavior, reducing insider threat and unauthorized access risks. - Unified Policy Management:
A single policy engine will allow organizations to define, monitor, and audit security controls across all workloads. - Secure Collaboration Across Clouds:
Cross-cloud identity federation will enable seamless, secure interactions between workloads on Google Cloud and other providers.
IAM Automation & Compliance Frameworks
- Automated Identity and Access Management (IAM):
Google is introducing enhanced automation within Cloud IAM, helping administrators manage permissions and roles with greater precision and less manual effort. - Policy Intelligence Enhancements:
- AI-driven insights to recommend least-privilege roles.
- Automated removal of unused service accounts or overly permissive access.
- AI-driven insights to recommend least-privilege roles.
- Compliance Framework Expansion:
Continuous alignment with industry standards such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, GDPR, and FedRAMP. - Custom Compliance Templates:
Organizations will be able to create and deploy policy templates that match their specific regulatory needs. - Continuous Compliance Monitoring:
Integrated tools like Security Command Center (SCC) will provide real-time compliance scoring and remediation recommendations. - Cross-Project Governance:
Unified identity and access control across multi-project environments for centralized management and auditability.
Data Security Enhancements
- Advanced Encryption Models:
All stored and transmitted data will continue to benefit from automatic encryption, with additional support for customer-managed and external encryption keys (CMEK & EKM). - Confidential Computing Expansion:
Google is extending confidential VM and container capabilities, ensuring sensitive workloads remain encrypted even during processing. - Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Upgrades:
Enhanced Cloud DLP API for real-time detection and masking of sensitive information across data streams and storage. - Integrated Threat Protection:
- Deeper integration between Chronicle Security Operations and Security Command Center.
- Unified threat detection and incident response across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Deeper integration between Chronicle Security Operations and Security Command Center.
- Data Sovereignty & Residency Controls:
Expanded regional data storage options to meet local compliance and privacy laws. - Secure AI and ML Governance:
Built-in tools for managing AI model security, ensuring compliance with ethical and regulatory frameworks.
2.5 Application Development & DevOps Cloud Run Improvements
- Enhanced Scalability and Performance:
Google is expanding Cloud Run capabilities to handle higher concurrency, faster cold starts, and more predictable scaling for production workloads. - Expanded Language and Framework Support:
Support for additional programming languages, frameworks, and runtimes to improve developer flexibility and deployment speed. - Deeper Integration with GKE and App Engine:
Seamless interoperability between Cloud Run, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and App Engine will simplify hybrid container-based development. - Improved Developer Experience:
- Simplified deployment from Git repositories using built-in CI/CD integration.
- More granular logging and monitoring through Cloud Logging and Cloud Trace.
- Simplified deployment from Git repositories using built-in CI/CD integration.
- Advanced Networking Features:
Integration with VPC connectors, private endpoints, and load balancing for secure and scalable application delivery. - Cost Optimization Tools:
Autoscaling based on real-time traffic metrics helps minimize operational costs while maintaining performance.
CI/CD Automation with Cloud Build
- End-to-End Automation:
Cloud Build will continue evolving as a fully managed CI/CD platform, offering faster build times, automated testing, and continuous delivery pipelines. - Pipeline Templates and Reusability:
Predefined build templates and reusable pipeline configurations will simplify setup and promote DevOps best practices. - Multi-Environment Deployments:
Enhanced integration with Artifact Registry, Cloud Deploy, and Anthos Config Management for deploying across multiple environments and clusters. - Security and Compliance in Pipelines:
- Built-in vulnerability scanning for container images and dependencies.
- Integration with Binary Authorization to ensure only trusted code reaches production.
- Built-in vulnerability scanning for container images and dependencies.
- Developer Productivity Enhancements:
Visual pipeline monitoring, parallel builds, and improved caching for faster iteration cycles. - GitOps Enablement:
Deeper integration with GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, supporting event-driven deployments and rollback mechanisms.
Microservices & API Integration
- API-First Development Approach:
Google is reinforcing API-centric development using Apigee API Management for designing, securing, and monitoring APIs at scale. - Service Mesh Expansion:
Anthos Service Mesh (ASM) improvements will provide advanced traffic management, observability, and zero-trust enforcement across microservices. - Unified Developer Toolchain:
Integrated toolsets across Cloud Code, Cloud Build, and Cloud Run streamline the development, deployment, and debugging process. - Observability and Tracing:
Enhanced Cloud Trace, Cloud Monitoring, and OpenTelemetry support to give developers deeper visibility into distributed applications. - Event-Driven Microservices:
Native eventing capabilities through Eventarc allow developers to build responsive, serverless microservices using real-time triggers. - Hybrid & Multicloud API Management:
Apigee and API Gateway will continue to expand cross-environment support for consistent API governance across hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures.
3️. How to Track GCP Updates Public Roadmap Dashboard
- Centralized Source of Upcoming Features:
Google provides an official Google Cloud Public Roadmap, a transparent dashboard that highlights new and planned features across all GCP services. - Feature Status Tracking:
Each item on the roadmap is labeled as Planned, In Development, In Preview, or Launched, helping users gauge feature maturity and release timelines. - Filter by Product or Category:
Users can filter roadmap items based on product lines—such as Compute, Storage, Networking, AI, or Security—to focus on specific areas of interest. - Search and Subscription Options:
Built-in search capabilities and subscription options enable users to receive notifications or updates about particular services. - Practical Use Case:
Businesses can use the roadmap to align their internal cloud migration or development plans with Google’s upcoming releases, ensuring early adoption where beneficial. - Access Point:
The roadmap is available publicly at cloud.google.com/roadmap, making it easy for anyone to explore new developments.
Release Notes
- Detailed Product-Level Updates:
GCP maintains release notes for each product, providing granular details about new features, patches, and bug fixes. - Frequent Updates:
Release notes are updated continuously, ensuring real-time visibility into changes that may affect production systems. - Version Control and Change Logs:
Each update includes version details, affected APIs, and configuration changes—critical for DevOps and operations teams. - Backward Compatibility Awareness:
Notes often include information on deprecated features or compatibility issues, allowing teams to prepare for smooth transitions. - Automation Possibility:
Users can subscribe via RSS feeds or integrate APIs to automatically track updates relevant to their environments. - Operational Benefit:
Regularly reviewing release notes helps organizations maintain compliance, reduce downtime, and take advantage of new functionalities as they launch.
Google Cloud Blog and Community
- Official Blog Insights:
The Google Cloud Blog is a key resource for announcements, product updates, customer success stories, and technical deep dives. - Expert Articles and Tutorials:
Posts authored by Google engineers and product teams provide practical insights, architecture guidance, and best practices for implementation. - Community Forums and Groups:
- Google Cloud Community, Reddit’s r/googlecloud, and Stack Overflow serve as platforms for collaboration and problem-solving.
- Users can discuss new roadmap items, share troubleshooting tips, and learn from real-world use cases.
- Google Cloud Community, Reddit’s r/googlecloud, and Stack Overflow serve as platforms for collaboration and problem-solving.
- Cloud Events and Webinars:
Google frequently hosts virtual events such as Cloud Next, Developer Summits, and webinars to showcase product innovations and roadmap updates. - Newsletter and Social Channels:
Following Google Cloud on LinkedIn, X (Twitter), and YouTube ensures consistent exposure to the latest product news and demonstrations. - Learning Advantage:
For learners and professionals, active participation in community discussions helps stay ahead of technology shifts and certification trends.
4️. GCP Learning Roadmap (Step-by-Step Path to Expertise)
Step 1: Build Foundational Knowledge Cloud Basics, Billing, and IAM
- Understand Cloud Fundamentals:
Begin with the core concepts of cloud computing — including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS — and how Google Cloud delivers these through its global infrastructure. - Familiarize with the GCP Console:
Learn to navigate the Google Cloud Console and Cloud Shell to manage and deploy resources efficiently. - Understand Billing and Pricing Models:
- Explore how GCP pricing works, including pay-as-you-go and sustained-use discounts.
- Learn to use the Pricing Calculator to estimate project costs.
- Study Billing Accounts and Budgets to control and optimize cloud spending.
- Explore how GCP pricing works, including pay-as-you-go and sustained-use discounts.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):
- Understand IAM roles, policies, and service accounts for secure access control.
- Learn how to assign permissions at project and resource levels.
- Practice implementing the principle of least privilege.
- Understand IAM roles, policies, and service accounts for secure access control.
- Recommended Learning Resources:
- Google Cloud Digital Leader Learning Path (Coursera, Google Cloud Skills Boost)
- Official documentation: “Google Cloud Fundamentals: Core Infrastructure”
- Google Cloud Digital Leader Learning Path (Coursera, Google Cloud Skills Boost)
Learn Core Services: Compute Engine and Cloud Storage
- Compute Engine (Virtual Machines):
- Learn how to create and manage VMs in the Compute Engine.
- Understand machine types, persistent disks, and image management.
- Practice deploying applications and configuring networking and firewalls
- Explore auto-scaling, load balancing, and instance templates for scalability.
- Learn how to create and manage VMs in the Compute Engine.
- Cloud Storage (Object Storage):
- Understand storage classes (Standard, Nearline, Coldline, Archive) and lifecycle rules.
- Learn how to upload, access, and secure data in Cloud Storage buckets.
- Explore versioning, data encryption, and IAM policies for Cloud Storage.
- Understand storage classes (Standard, Nearline, Coldline, Archive) and lifecycle rules.
- Hands-on Practice:
- Deploy a sample application using Compute Engine and store data in Cloud Storage.
- Experiment with cost monitoring and IAM configurations in a sandbox project.
- Deploy a sample application using Compute Engine and store data in Cloud Storage.
- Recommended Learning Resources:
- Google Cloud Skills Boost Labs: “Create and Manage Cloud Resources”
- Coursera Course: “Google Cloud Fundamentals: Core Infrastructure”
- Documentation: Compute Engine Overview and Cloud Storage Basics
Step 2: Develop Practical Skills Qwiklabs / Google Cloud Skills Boost Labs
- Hands-On Learning Environment:
Google Cloud Skills Boost (formerly Qwiklabs) provides interactive, real-world cloud environments where learners can practice deploying and managing resources without risk. - Guided Labs and Quests:
- Quests are structured learning paths made up of multiple labs that focus on specific GCP technologies or roles (e.g., Data Engineer, Cloud Architect, DevOps Engineer).
- Labs offer time-limited access to actual GCP environments — not simulations — ensuring genuine experience with the platform.
- Quests are structured learning paths made up of multiple labs that focus on specific GCP technologies or roles (e.g., Data Engineer, Cloud Architect, DevOps Engineer).
- Key Learning Topics to Focus On:
- Creating and managing virtual machines (Compute Engine)
- Building and deploying containerized applications with Cloud Run or GKE
- Setting up IAM roles, service accounts, and access control
- Using Cloud Monitoring and Cloud Logging for visibility and troubleshooting
- Creating and managing virtual machines (Compute Engine)
- Skill Badges and Progress Tracking:
Completing labs and quests earns Google Cloud skill badges, which can be displayed on professional profiles such as LinkedIn. - Recommended Quests for Beginners:
- “Baseline: Infrastructure”
- “Getting Started with Cloud Shell and gcloud”
- “Cloud Engineering”
- “BigQuery for Data Analysts”
Deploy Simple Workloads (Web App, Database, Logging)
- Web Application Deployment:
- Build and deploy a simple web application using App Engine or Cloud Run.
- Learn how to configure environment variables, versioning, and scaling settings.
- Set up load balancing for high availability and performance.
- Build and deploy a simple web application using App Engine or Cloud Run.
- Database Setup and Integration:
- Deploy Cloud SQL for relational databases or Firestore for NoSQL workloads.
- Practice connecting applications securely using private IPs and service accounts.
- Learn to perform basic operations — creating tables, writing queries, and backing up data.
- Deploy Cloud SQL for relational databases or Firestore for NoSQL workloads.
- Logging and Monitoring Setup:
- Implement Cloud Logging to capture system and application logs.
- Use Cloud Monitoring dashboards to track performance metrics.
- Set up alerts for CPU usage, storage, or error rates to ensure proactive issue detection.
- Implement Cloud Logging to capture system and application logs.
- Infrastructure as Code (Optional Advanced Practice):
Use Terraform or Deployment Manager to automate the provisioning of resources. - Practical Goal:
By completing this step, learners will be able to build and manage small-scale, production-ready applications while understanding the end-to-end deployment workflow on GCP.
Step 3: Explore Key Specializations Compute | Networking | Data | Security | AI/ML
- Compute Specialization:
- Deepen your knowledge of Compute Engine, App Engine, and Cloud Run for scalable application hosting.
- Learn about Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for container orchestration and microservice management.
- Understand autoscaling, load balancing, and infrastructure optimization techniques.
- Deepen your knowledge of Compute Engine, App Engine, and Cloud Run for scalable application hosting.
- Networking Specialization:
- Study VPC networks, subnets, firewalls, and Cloud DNS.
- Learn about Cloud Interconnect, Cloud VPN, and Private Service Connect for hybrid connectivity.
- Explore network security, latency optimization, and load balancing best practices.
- Study VPC networks, subnets, firewalls, and Cloud DNS.
- Data Specialization:
- Focus on BigQuery, Cloud SQL, Firestore, and Dataflow for analytics and data processing.
- Learn ETL pipeline design and data warehousing concepts.
- Understand data governance using Dataplex and BigLake.
- Focus on BigQuery, Cloud SQL, Firestore, and Dataflow for analytics and data processing.
- Security Specialization:
- Master IAM, VPC Service Controls, Cloud KMS, and Security Command Center.
- Learn about Zero Trust principles, policy automation, and compliance monitoring.
- Explore encryption models, key management, and threat detection within GCP.
- Master IAM, VPC Service Controls, Cloud KMS, and Security Command Center.
- AI/ML Specialization:
- Dive into Vertex AI, BigQuery ML, and Gemini AI integrations.
- Build and deploy predictive and generative AI models using Google’s pre-trained APIs.
- Learn MLOps best practices — from training and deployment to monitoring and governance.
- Dive into Vertex AI, BigQuery ML, and Gemini AI integrations.

Pick Your Learning Path
Depending on your career interests and goals, choose a focused learning path that aligns with your desired role.
- System Administrator:
- Learn how to manage GCP projects, users, and resources efficiently.
- Focus on automation, monitoring, and system security.
- Recommended certification: Associate Cloud Engineer.
- Learn how to manage GCP projects, users, and resources efficiently.
- Kubernetes Administrator:
- Gain expertise in deploying and managing containerized applications using GKE.
- Learn cluster scaling, service mesh integration, and CI/CD automation.
- Recommended certification: Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) or GCP Professional Cloud Architect.
- Gain expertise in deploying and managing containerized applications using GKE.
- DevOps Engineer:
- Master Cloud Build, Cloud Deploy, Artifact Registry, and Terraform for infrastructure automation.
- Learn continuous integration, testing, and delivery workflows.
- Recommended certification: Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer.
- Master Cloud Build, Cloud Deploy, Artifact Registry, and Terraform for infrastructure automation.
- Site Reliability Engineer (SRE):
- Focus on monitoring, incident management, and reliability engineering principles.
- Learn to balance reliability, scalability, and performance with service-level objectives (SLOs).
- Recommended certification: Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer.
- Focus on monitoring, incident management, and reliability engineering principles.
- Data Engineer:
- Learn data ingestion, transformation, and analytics pipelines using BigQuery, Dataflow, and Pub/Sub.
- Study real-time data processing and storage optimization.
- Recommended certification: Professional Data Engineer.
- Learn data ingestion, transformation, and analytics pipelines using BigQuery, Dataflow, and Pub/Sub.
Step 4: Advanced Tools & Real-World Use Terraform (Infrastructure as Code - IaC)
- Automate Cloud Infrastructure:
- Learn how to define, provision, and manage Google Cloud resources using Terraform.
- Understand how Infrastructure as Code (IaC) ensures consistency, repeatability, and version control across environments.
- Learn how to define, provision, and manage Google Cloud resources using Terraform.
- Core Skills to Build:
- Write and organize Terraform configuration files (.tf).
- Manage variables, outputs, and modules for reusable templates.
- Use Terraform Cloud or CI/CD pipelines for automated deployments.
- Write and organize Terraform configuration files (.tf).
- Integration with GCP:
- Practice deploying Compute Engine instances, networking components, and IAM policies using Terraform.
- Learn how to integrate Terraform with Cloud Build and GitHub Actions for DevOps workflows.
- Practice deploying Compute Engine instances, networking components, and IAM policies using Terraform.
- Practical Tip:
Start by automating a small GCP environment and then scale up to multi-project automation.
Cloud Monitoring + Cloud Logging
- Unified Observability:
- Learn to monitor performance, uptime, and resource utilization using Cloud Monitoring.
- Capture and analyze system and application logs using Cloud Logging.
- Key Features to Explore:
- Metrics & Dashboards: Create custom dashboards to visualize performance metrics.
- Alerting Policies: Set up automated alerts for CPU spikes, latency issues, or downtime.
- Error Reporting & Trace: Diagnose application errors and latency bottlenecks in distributed systems.
- Best Practices:
- Implement centralized logging for all services.
- Use log-based metrics for smarter monitoring.
- Integrate monitoring with incident response workflows (e.g., PagerDuty or Slack)
BigQuery & Real-Time Pipelines
- BigQuery for Data Analytics:
- Deepen your understanding of BigQuery architecture, query optimization, and partitioning.
- Learn how to integrate BigQuery with Dataflow, Pub/Sub, and Looker Studio for end-to-end analytics.
- Building Real-Time Data Pipelines:
- Stream data using Pub/Sub and process it in real-time with Dataflow.
- Implement ETL and ELT pipelines for analytics and AI workloads.
- Learn BigQuery ML for in-database machine learning and predictive analytics.
- Hands-on Projects:
- Build a streaming dashboard for real-time analytics.
- Analyze cost and performance of large datasets using partitioned tables.
Cost Optimization (FinOps)
- Shift Toward Serverless Architectures:
- The future of application development on GCP lies in fully managed, event-driven, and auto-scaling services.
- Offerings like Cloud Run, Cloud Functions, and Firebase Hosting eliminate infrastructure overhead, enabling faster development cycles.
- Advantages of Serverless Adoption:
- Pay only for what you use — improved cost efficiency and scalability.
- Simplified deployment with automatic scaling and version control.
- Seamless integration with GCP services like Pub/Sub, Firestore, and BigQuery.
- Serverless + AI/ML Integration:
- Expect tighter integration between serverless computing and AI pipelines, enabling real-time inference, automation, and intelligent data processing.
- Best Practice for Teams:
- Start modernizing legacy applications into microservices and serverless workloads.
- Combine serverless design with event-driven architectures for agility and resilience.
5️. Certification Roadmap Best Order for Career Growth
Google Cloud certifications validate your technical expertise and help you advance your career in cloud engineering, DevOps, data, and AI. Below is the recommended order to follow, from foundational to advanced levels.
Beginner Level Certification: Google Cloud Digital Leader Who Should Choose It:
- Non-technical professionals, business leaders, and beginners exploring cloud concepts.
- Anyone looking to understand the fundamentals of cloud computing, GCP core services, and business value of the cloud.
What You’ll Learn: - Foundational cloud concepts and Google Cloud’s service categories.
- Pricing models, security basics, and resource management.
- High-level understanding of digital transformation with Google Cloud.
Preparation Resources: - Course: Google Cloud Digital Leader Training (Coursera / Skill Boost)
- Study material: Official Exam Guide + Practice Tests

Core Level Certification: Associate Cloud Engineer (ACE) Who Should Choose It:
- Cloud administrators, DevOps beginners, and IT professionals managing GCP environments.
- Ideal for those seeking hands-on deployment and operations experience.
What You’ll Learn: - Deploying applications, managing projects, and configuring IAM permissions.
- Monitoring resources and managing billing within the Google Cloud Console and CLI.
- Foundational DevOps and automation workflows.
Preparation Resources: - Google Cloud Skills Boost – Associate Cloud Engineer Learning Path
- Practice labs on Compute Engine, Cloud Storage, IAM, and Cloud Monitoring.
- Mock tests and sample case studies.
Professional Level Certifications:
- Professional Cloud Architect
- Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer
- Professional Data Engineer
- Professional Security Engineer
- Professional Cloud Network Engineer
- Professional Machine Learning Engineer
Who Should Choose It:
- Experienced cloud professionals looking for role-based specialization.
- Senior engineers and architects aiming for leadership and high-impact technical roles.
What You’ll Learn (Depending on Track):
- Cloud Architect: Solution design, scalability, and governance strategies.
- DevOps Engineer: CI/CD pipelines, reliability engineering, and SRE practices.
- Data Engineer: Data warehousing, ETL pipelines, and AI/ML integration with BigQuery and Vertex AI.
- Security Engineer: Identity management, Zero Trust, compliance, and threat prevention.
- ML Engineer: Model development, deployment, and monitoring using Vertex AI.
Preparation Resources: - Google Cloud Professional Certification Paths (Skill Boost)
- Hands-on labs, mock exams, and scenario-based study material.
- Case studies from Google Cloud documentation.
Study Communities & Exam Tips
- Join Study Groups:
- Engage in GCP study communities on Reddit, LinkedIn, and Discord.
- Join local Google Developer Groups (GDG) or Cloud Study Jams for guided preparation.
- Engage in GCP study communities on Reddit, LinkedIn, and Discord.
- Use Practice Labs Regularly:
- Reinforce concepts through real-world labs on Google Cloud Skills Boost (Qwiklabs).
- Focus on the practical application of theory — not just memorization.
- Reinforce concepts through real-world labs on Google Cloud Skills Boost (Qwiklabs).
- Exam Preparation Tips:
- Review case studies and understand architectural trade-offs.
- Practice using the gcloud CLI extensively.
- Use official exam guides and practice tests for time-bound mock sessions.
- Focus on security, networking, and automation concepts, which appear frequently in advanced exams.
- Review case studies and understand architectural trade-offs.
- Keep Skills Current:
- Certifications remain valid for 2 years.
- Stay updated through Google Cloud Blog, release notes, and training refreshers.
- Certifications remain valid for 2 years.
6️ Real-World Cloud Implementation Migrating Workloads to GCP
- Assessment & Planning:
- Begin by assessing existing on-premises or multi-cloud workloads.
- Identify which applications are suitable for lift-and-shift, re-platforming, or re-architecting.
- Use tools like Migrate to Virtual Machines (Migrate to Compute Engine) for smooth VM migration.
- Begin by assessing existing on-premises or multi-cloud workloads.
- Execution Strategy:
- Start with low-risk workloads and expand progressively.
- Leverage Database Migration Service (DMS) for seamless database transitions.
- Migrate storage and data using Transfer Appliance, Storage Transfer Service, or gsutil.
- Start with low-risk workloads and expand progressively.
- Post-Migration Optimization:
- Test application performance and validate IAM policies.
- Optimize cost and performance using autoscaling, load balancing, and sustained-use discounts.
- Implement monitoring and alerting to ensure smooth operation after migration.
- Test application performance and validate IAM policies.
Scalability & High Availability
- Design for Elastic Growth:
- Use Compute Engine Autoscaler, Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler, or Cloud Run concurrency settings for dynamic scaling.
- Implement global load balancing to distribute traffic efficiently across regions.
- Use Compute Engine Autoscaler, Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler, or Cloud Run concurrency settings for dynamic scaling.
- High Availability (HA) Best Practices:
- Deploy workloads across multiple zones and regions to avoid single points of failure.
- Use Cloud SQL High Availability configurations and Regional Persistent Disks for resilience.
- Implement backup and disaster recovery (DR) strategies using Snapshots and Coldline Storage.
- Deploy workloads across multiple zones and regions to avoid single points of failure.
- Performance Optimization:
- Use Cloud CDN for faster content delivery.
- Monitor latency and throughput using Cloud Monitoring dashboards.
- Continuously test scalability under simulated loads.
- Use Cloud CDN for faster content delivery.
Security-First Design
- Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP):
- Assign IAM roles carefully — avoid granting excessive permissions.
- Use service accounts, organization policies, and resource hierarchy for structured access control.
- Assign IAM roles carefully — avoid granting excessive permissions.
- Network & Data Protection:
- Implement VPC Service Controls, firewall rules, and Private Google Access.
- Encrypt data both in transit (TLS) and at rest (KMS-managed keys).
- Use Cloud Armor for DDoS protection and Security Command Center for threat visibility.
- Implement VPC Service Controls, firewall rules, and Private Google Access.
- Compliance & Governance:
- Apply policies using Cloud Asset Inventory and Policy Intelligence.
- Regularly audit configurations using Forseti or Cloud Config Connector.
- Maintain alignment with frameworks such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR.
- Apply policies using Cloud Asset Inventory and Policy Intelligence.
Cost-Saving Strategies
- Resource Optimization:
- Identify idle or underutilized resources using Recommender API and Billing Reports.
- Use Preemptible VMs for batch processing and Committed Use Discounts for predictable workloads.
- Storage & Data Management:
- Implement lifecycle management for Cloud Storage buckets to automatically move infrequently used data to cheaper classes.
- Use BigQuery cost controls such as partitioned tables and query limits.
- Monitoring & Governance:
- Set up budgets and alerts to stay within financial limits.
- Use FinOps dashboards to visualize and manage costs across projects.
- Continuously review billing reports to identify optimization opportunities.
- Culture of Cost Awareness:
- Encourage teams to tag resources and take ownership of their spend.
- Adopt FinOps practices — combining financial accountability with technical efficiency.
7️. Challenges & Best Practices Staying Up to Date with Rapid Changes
- Continuous Learning is Essential:
- Google Cloud evolves rapidly — with frequent service updates, new features, and changing best practices.
- Make continuous learning part of your workflow by setting aside time each week for reading release notes or exploring new tools.
- Official Sources to Follow:
- Google Cloud Blog: Regular updates on product launches, use cases, and architecture insights.
- Release Notes & Roadmap Dashboard: Track service-level updates and upcoming chang
- YouTube & Cloud Podcasts: Access technical talks and real-world implementation case studies.
- Community Engagement:
- Join Google Developer Groups (GDGs), Reddit, LinkedIn, or Discord communities to exchange knowledge.
- Participate in Google Cloud events, Next conferences, and Cloud Study Jams to stay current.
Practical Tip:
Subscribe to Google Cloud’s monthly newsletters and set up alerts for service updates relevant to your projects.
Avoiding Unnecessary Complexity
- Adopt a “Simplicity-First” Mindset:
- Cloud architectures should be scalable and maintainable — not over-engineered.
- Start small, validate with proofs of concept (POCs), and then scale gradually.
- Standardize and Automate:
- Use Terraform or Deployment Manager for consistent provisioning.
- Maintain clear documentation and version control for all configurations.
- Implement templates and service catalogs to reduce redundancy across teams.
- Avoid Common Pitfalls:
- Don’t mix too many overlapping services (e.g., multiple data tools for the same use case).
- Keep network and IAM designs clean and modular.
- Monitor cost implications when adding new services or regions.
- Best Practice:
Simplify wherever possible — the best architectures are often the ones easiest to understand, secure, and maintain.

Ensuring Governance & Security from Day 1
- Establish Clear Governance Frameworks:
- Define organization hierarchy (Organization → Folders → Projects) early in your setup.
- Implement resource naming conventions, labels, and billing structure for clarity.
- Security-First Implementation:
- Apply IAM roles, service accounts, and policies immediately after project creation.
- Enforce VPC Service Controls to protect sensitive data and prevent data exfiltration.
- Use Cloud Armor, KMS, and Security Command Center for layered protection.
- Compliance and Audit Readiness:
- Use Cloud Audit Logs and Cloud Asset Inventory to maintain traceability.
- Regularly review access permissions and update based on least-privilege principles.
- Align with compliance standards (ISO, SOC, GDPR) through automated checks.
- Cultural Best Practice:
- Make security a shared responsibility across teams.
- Encourage developers, DevOps, and data teams to treat governance as part of their daily workflow — not as an afterthought.
8️. Future Trends in GCP AI-Driven Infrastructure Automation
- Rise of Intelligent Cloud Operations:
- Google Cloud is integrating AI and machine learning into every layer of infrastructure management.
- Expect AI-driven automation in scaling, performance tuning, and predictive maintenance.
- Google Cloud is integrating AI and machine learning into every layer of infrastructure management.
- Autonomous Cloud Management:
- Tools like Gemini for Google Cloud and Vertex AI will enhance operational efficiency by analyzing system metrics and automatically resolving issues.
- Predictive algorithms will forecast demand spikes, optimize workloads, and prevent outages before they occur.
- Tools like Gemini for Google Cloud and Vertex AI will enhance operational efficiency by analyzing system metrics and automatically resolving issues.
- Impact on Cloud Roles:
- Traditional DevOps roles will evolve toward AIOps (AI for IT Operations) — focusing on automation, insights, and governance rather than manual intervention.
- Engineers will spend more time designing intelligent workflows and less time on repetitive management tasks.
- Traditional DevOps roles will evolve toward AIOps (AI for IT Operations) — focusing on automation, insights, and governance rather than manual intervention.
- Best Practice for the Future:
Begin exploring AI-integrated tools such as Vertex AI Workbench, Cloud Operations Suite, and Generative AI APIs to stay ahead in automation-driven cloud environments.
Serverless Era Dominance
- Shift Toward Serverless Architectures:
- The future of application development on GCP lies in fully managed, event-driven, and auto-scaling services.
- Offerings like Cloud Run, Cloud Functions, and Firebase Hosting eliminate infrastructure overhead, enabling faster development cycles.
- Advantages of Serverless Adoption:
- Pay only for what you use — improved cost efficiency and scalability.
- Simplified deployment with automatic scaling and version control.
- Seamless integration with GCP services like Pub/Sub, Firestore, and BigQuery.
- Serverless + AI/ML Integration:
- Expect tighter integration between serverless computing and AI pipelines, enabling real-time inference, automation, and intelligent data processing.
- Best Practice for Teams:
- Start modernizing legacy applications into microservices and serverless workloads.
- Combine serverless design with event-driven architectures for agility and resilience.
SustaiCloudnable & Energy-Efficient
- Sustainability as a Core Priority:
- Google Cloud is committed to operating on carbon-free energy (CFE) 24/7 by 2030.
- Expect more features in the Carbon Footprint Dashboard and APIs to help organizations measure and reduce emissions.
- Green Data Centers & Resource Optimization:
- GCP data centers already operate at high Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) using renewable energy sources.
- Future innovations will optimize resource allocation dynamically to reduce waste.
- Eco-Conscious Cloud Architecture:
- Developers will increasingly adopt sustainability-focused design principles — choosing energy-efficient regions, optimizing compute resources, and managing data retention responsibly.
- Enterprise Impact:
- Companies can align with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals by leveraging GCP’s sustainability tools and reporting capabilities.
- Expect sustainability to become a key KPI in cloud architecture decisions.
- Best Practice:
Regularly review your workloads for energy efficiency and leverage Google Cloud’s sustainability APIs to track and reduce your carbon footprint.
9️ .Conclusion Importance of Leveraging GCP Advancements
- Staying Competitive in the Cloud Era:
- The pace of innovation in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) continues to accelerate — from AI-powered infrastructure to serverless and sustainable computing.
- Businesses and professionals who adapt early gain a significant advantage in performance, scalability, and cost efficiency.
- The pace of innovation in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) continues to accelerate — from AI-powered infrastructure to serverless and sustainable computing.
- Continuous Transformation:
- Leveraging GCP’s evolving ecosystem allows organizations to innovate faster, streamline operations, and deliver better customer experiences.
- Individuals who stay updated with the platform’s roadmap position themselves for long-term career growth and technical leadership.
- Leveraging GCP’s evolving ecosystem allows organizations to innovate faster, streamline operations, and deliver better customer experiences.
- Strategic Takeaway:
Embrace GCP advancements not just as tools, but as enablers of transformation — driving smarter architectures, data-driven insights, and sustainable solutions.
Encourage Learning + Using Roadmap Insights
- For Learners:
- Use this roadmap as a structured path — from fundamentals to professional mastery.
- Combine theory with hands-on practice using Google Cloud Skills Boost and real-world projects.
- Keep refining your skills as new technologies emerge across AI, DevOps, and data.
- For Learners:
- For Businesses:
- Align your IT and business strategies with GCP’s technology roadmap.
- Focus on security, automation, and cost optimization to maximize ROI.
- Encourage team learning and certification to build internal cloud expertise.
- Mindset for Success:
Treat cloud learning as a journey, not a one-time goal. The more you explore, the more value you unlock from GCP.
Call to Action: Explore GCP Roadmap → Start Building Today
- Get Started Now:
- Begin wi foundational GCP concepts and labs on Google Cloud Skills Boost.
- Choose your specialization — whether it’s architecture, data engineering, AI/ML, or DevOps — and follow the roadmap step-by-step.
- Begin wi foundational GCP concepts and labs on Google Cloud Skills Boost.
- Engage with the Ecosystem:
- Join GCP communities, attend webinars, and contribute to open-source cloud projects.
- Follow Google Cloud Blog and roadmap updates to stay ahead of new trends.
- Join GCP communities, attend webinars, and contribute to open-source cloud projects.
- Build for the Future:
- The cloud landscape will continue to evolve — AI-driven automation, serverless platforms, and sustainability will shape what’s next.
- The cloud landscape will continue to evolve — AI-driven automation, serverless platforms, and sustainability will shape what’s next.
- Start implementing what you’ve learned today to design reliable, scalable, and future-ready solutions on Google Cloud.
FAQs
It’s Google Cloud’s official plan outlining upcoming features, tools, and innovations.
It helps users stay informed about what’s next in cloud computing.
It helps businesses align strategies with Google’s evolving technologies.
Developers can plan ahead and prepare for future updates.
The roadmap is available at cloud.google.com/roadmap.
It lists features as Planned, In Development, or Launched.
Google updates it every few weeks or months.
New features and community feedback drive these updates.
AI, multicloud, analytics, security, and sustainability.
These pillars guide Google Cloud’s innovation journey.
Faster VMs, confidential computing, and better autoscaling.
Upgraded GPUs and TPUs improve AI workloads.
GKE Autopilot now offers smarter scaling and cost control.
Anthos enhances hybrid management and container orchestration.
BigQuery Omni supports cross-cloud data analysis.
AI-powered queries and real-time analytics are coming soon.
Vertex AI and Gemini simplify model training and deployment.
AI tools are becoming more accessible to all users.
Gemini powers generative AI, automation, and coding assistance.
It integrates deeply with Vertex AI and BigQuery.
Zero Trust, IAM automation, and data encryption are key.
AI-driven Security Command Center enhances threat detection.
Anthos simplifies multicloud operations and workload portability.
BigQuery Omni enables cross-cloud analytics on AWS and Azure.
It offers billing dashboards, AI cost tips, and FinOps tools.
Predictive analytics help forecast and manage expenses.
Google gathers input from users, partners, and CSMs.
This feedback shapes roadmap priorities and improvements.
Planned means upcoming, In Development is being built, Launched is live.
These statuses help users plan technology adoption.
Yes, through feedback, beta programs, and enterprise input.
Google values customer collaboration for roadmap direction.
They can align migration and deployment plans with updates. It helps avoid deprecated services and design future-proof systems.
It provides transparency into future releases and support.
This helps teams plan safely and avoid service disruptions.
The roadmap highlights AI, analytics, and automation tools.
These drive innovation and faster modernization for businesses.
New releases improve app speed, security, and compatibility.
Developers can adapt early to maintain performance.

