A Step-by-Step Guide to the GCP Pricing Calculator
In this article, we’ll explore the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Pricing Calculator in detail. We’ll break down its key features and functions, and explain how to use it to estimate costs for various GCP services. Whether you’re new to GCP or have some experience, our goal is to help you effectively manage and predict your cloud expenses using this powerful tool.
Gcp Pricing Calculator

Contents

Introduction
Overview of Cloud Cost Management
As companies move their systems to the cloud, keeping track of cloud expenses is crucial for all types of organisations. The flexible pricing options and numerous services from cloud providers can make cost management tricky. The GCP Pricing Calculator assists users in estimating and controlling their costs efficiently. This part highlights why managing costs in the cloud is important, the difficulties in predicting expenses because of complex pricing, and the value of tools like the GCP Pricing Calculator for easier cost predictions.
What is the GCP Pricing Calculator?
The GCP Pricing Calculator is an essential tool for both new and experienced Google Cloud users. It allows users to estimate the cost of Google Cloud Platform services by selecting from a range of products and configurations. This section introduces the tool, explaining its core functionality, how it simplifies cost planning, and its relevance for organisations aiming to control their cloud expenses.
Understanding Google Cloud Platform's Pricing Structure
Overview of GCP Pricing
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) uses a pay-as-you-go system, so you only pay for what you use. This section explains the key parts of GCP’s pricing, such as compute, storage, and networking, which influence your cloud costs. We will also compare GCP’s pricing with other big cloud services like AWS and Azure to show how it compares in the market
GCP provides various features and discounts that can help users save money. This part explores important ideas like:
Sustained Use Discounts : Discounts that apply automatically when you use certain services for a long time.
Committed Use Contracts: Agreements that let you use specific resources for a long time in return for big savings.
Preemptible VMs: These are affordable computing choices that work well for tasks that need to keep running even if they are interrupted.
Free Tier Usage: An overview of the resources available for free under GCP’s always-free tier, as well as introductory credits for new users.
Navigating the GCP Pricing Calculator
Getting Started with the Pricing Calculator : This chapter starts by explaining how to access and use the GCP Pricing Calculator. It guides you through the tool’s layout, covering different parts like choosing services, selecting regions, and understanding pricing. By the end, users will know how to use the tool effectively.
Setting Up a Basic Estimate : This part provides a simple guide to making a pricing estimate with the calculator. It includes an example, like figuring out the cost of a basic virtual machine (VM) instance. You will learn how to choose services, regions, and set options. This guide is useful for users to start making their own estimates.
Understanding the Estimate Summary : After the pricing estimate is created, it’s important to understand the results correctly. This part explains the summary of the estimate, showing how to read the monthly and yearly cost estimates, total prices for various setups, and how different elements can influence pricing.
Pricing Estimates for Key GCP Services
Compute Engine Pricing : Compute Engine is a fundamental service in GCP, and its costs vary based on factors like machine types, locations, and discounts such as sustained use and preemptible options. This part explains how to calculate expenses for different workloads, including web hosting and machine learning, with examples to help create precise pricing estimates for various scenarios.
Cloud Storage Pricing : This section outlines the pricing for Cloud Storage, detailing the costs associated with different storage classes (Standard, Nearline, Coldline, Archive), data retrieval, and network egress. An example, like estimating the cost of an object storage solution, aids users in grasping how these pricing elements work in practice.
BigQuery Pricing : BigQuery features a flexible pricing structure, offering both on-demand and flat-rate options. This section clarifies how BigQuery pricing operates and provides a scenario for estimating costs related to an analytics workload, assisting users in choosing the most suitable pricing model for their requirements.
Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Pricing : GKE pricing is influenced by factors such as node pools, autoscaling, and networking. This section examines the pricing aspects of Kubernetes clusters, presenting an example of pricing a microservices architecture to illustrate how various choices impact costs.
Cloud Functions and Serverless Pricing : Serverless offerings like Cloud Functions, Cloud Run, and App Engine have distinct pricing models based on request counts, compute time, and memory usage. This section provides guidance on estimating costs for a serverless web application, helping users plan for serverless workloads effectively.
Networking Costs : GCP incurs charges for network egress, inter-region traffic, and load balancing. This section details networking costs and includes an example of estimating expenses for a multi-region deployment with high network traffic.
Cloud SQL and Database Services Costs : Database services, including Cloud SQL, Spanner, and Firestore, have costs that depend on factors like the type of instance, storage size, and network usage. For instance, you can estimate the expenses for setting up a relational database by using the pricing calculator designed for these services.
AI and Machine Learning Costs : On GCP, AI and machine learning services like AI Platform and AutoML have costs based on how much resources are used during training and making predictions. This part shows how to calculate costs for machine learning projects and provides an example of pricing a machine learning task using AI Platform.
Enhanced Features and Custom Options
Custom Machine Types and Storage Choices : GCP lets users create tailored machine types and set up specific disk options for their unique workloads. This part explains how to configure and price these custom setups using the GCP Pricing Calculator.
Including Sustained Use and Committed Use Discounts : This section shows how to factor in sustained use discounts and committed use agreements in your pricing estimates, helping you save money over the long term.
Managing Complex Workloads : Pricing for complex setups with multiple services can be tricky. This section provides an example of pricing a multi-service system, showing how to consider the relationships between compute, storage, and networking in your cost calculations.
Exporting and Sharing Estimates : The GCP Pricing Calculator enables users to export their estimates for reports or share them with colleagues. This section details how to export and share pricing estimates to improve teamwork and decision-making.
Best Ways to Use the GCP Pricing Calculator
Saving Money on Cloud Costs with the Calculator : This part shares tips for finding ways to save money using the pricing calculator, like selecting the best regions, improving resource use, and using discounts.
Adding the Pricing Calculator to Your Cloud Plan : This part looks at how to include the pricing calculator in your overall cloud plan, aiding in planning, budgeting, and making choices. It also explains how to use the calculator to track and predict cloud spending.
Frequent Mistakes to Watch Out For : Ignoring important factors such as data transfer and storage costs can result in underestimating cloud bills. This part points out common mistakes and gives tips on how to avoid them.
Using Google Cloud Support and Tools : Google Cloud provides various extra tools and resources for managing costs, including the Billing Console and Cost Management APIs. This part gives a summary of these tools and shows how to use them alongside the GCP Pricing Calculator for better cost management.
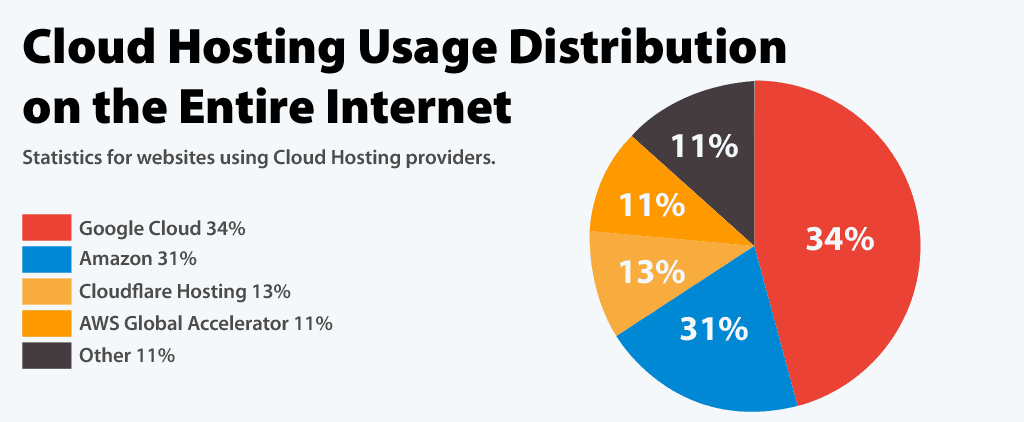
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Managing Cloud Costs for Startups : Startups must keep a close eye on their cloud expenses as they grow. This example illustrates how a developing e-commerce site can utilise the GCP Pricing Calculator to reduce costs, showcasing effective cloud cost management for startups.
Example 2: Multi-Cloud Approach for Enterprises : Many enterprises choose multi-cloud solutions to fulfil their business requirements. This example examines how a company can use the GCP Pricing Calculator to evaluate costs from various cloud providers, including a case of a hybrid cloud setup that combines GCP with on-site resources.
Example 3: Budgeting for Cloud Resources in Education : Educational institutions often need to plan their cloud spending for research or student projects. This example shows how a school can use the GCP Pricing Calculator to budget for a significant research initiative, highlighting practical cloud cost management in the education sector.

Customising Price Estimates
Setting Up Advanced Options
Custom Machine Types: Learn how to create and set up custom machine types tailored to specific workload needs. Explore various CPU, memory, and GPU setups.
Custom Storage Classes: Get to know and set up custom storage choices for better performance and cost efficiency.
Network Setup: Estimating costs for various network configurations, including VPNs, interconnects, and custom routing.
Optimising for Unique Use Cases
High-Performance Computing (HPC): Discover how to estimate costs for high-performance tasks like large-scale simulations and data processing.
Big Data Solutions: Calculate expenses for big data processing using tools such as Dataproc and Dataflow, covering data ingestion, processing, and storage.
IoT Deployments: Estimate costs for IoT projects, including device management, data ingestion, and analytics.
Cost Estimation for Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Hybrid Cloud Setups: Create estimates for hybrid cloud systems that combine GCP with on-premises infrastructure.
Multi-Cloud Scenarios: Compare costs among various cloud providers in a multi-cloud approach. Explore tools and strategies for managing costs in a multi-cloud setting.
Financial Management and Cost Control Methods
Budgeting and Predictions
Creating Budgets: Establishing budgets in the GCP Billing Console and tracking compliance with budget limits.
Cost Predictions: Leveraging past data and trends to estimate future cloud expenses and plan for growth.
Alerts and Notifications
Setting Up Alerts: Configuring alerts and notifications to keep an eye on spending and prevent unexpected fees.
Thresholds and Notifications: How to set spending limits and get alerts when nearing or surpassing budget thresholds.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Rightsizing Resources: Methods for reviewing and adjusting resource sizes to fit actual usage and prevent over-allocation.
Idle Resource Management: Finding and managing unused or underused resources to cut costs.
Cost Allocation Tags: Applying tags to assign costs to specific projects or departments for improved financial clarity.
Connecting with External Tools and Services
Cost Management Tools
External Cost Management Solutions: A look at well-known tools such as Cloudability, CloudHealth, and Spot.io that help improve cost management and optimization.
Linking with Financial Systems: Steps to connect GCP cost information with financial management systems for better reporting and analysis.
API Integration
Utilising the GCP Billing API: Instructions on how to programmatically retrieve detailed cost information using GCP’s Billing API for tailored reporting and analysis.
Automation and Scripting: Using scripts and tools to automate cost management tasks, making cost control processes more efficient.
Advanced Cost Management Methods
Using Machine Learning and AI for Cost Savings
Forecasting Costs: Applying machine learning to estimate future cloud expenses based on past usage trends.
Automated Cost Savings: Using AI tools and algorithms for ongoing cost savings and resource management.
Cost Control and Compliance
Establishing Cost Control Policies: Creating policies to ensure that cost management best practices are followed throughout the organisation.
Compliance Checks: Conducting regular reviews of cloud spending to ensure it meets financial policies and regulations.
Examples and Insights
Practical Cost Savings: Insights from businesses that have effectively reduced their cloud costs with advanced methods and strategies.
Frequent Mistakes: Common errors in cost management and tips on how to avoid them.

Community and Expert Insights
Expert Views: Perspectives from cloud specialists and consultants on effective ways to use the GCP Pricing Calculator and control cloud expenses.
Market Trends: Recent trends and forecasts in cloud pricing and cost management.
Community Input and Experiences
User Stories: Accounts from GCP users on how they successfully handle their cloud expenses.
Discussion Boards: Showcasing lively forums and groups where users exchange tips and guidance on utilising the GCP Pricing Calculator.
Future Trends and New Ideas
Changing Pricing Structures
What’s Coming: A look at expected shifts in GCP pricing models and their effects on managing costs.
New Developments in Cloud Pricing: An examination of fresh technologies and methods in cloud pricing and what they mean for users.
Staying Informed
How to Stay Updated: Suggestions for keeping track of the newest features and updates to the GCP Pricing Calculator.
Educational Materials: Suggested resources, courses, and certifications to enhance your knowledge of cloud cost management.
Cost Management for Different Industries
Healthcare Sector
Regulatory Compliance: Estimating costs for healthcare solutions while following rules like HIPAA.
Use Cases: Pricing examples for electronic health records (EHR) systems, telemedicine services, and patient care data analytics.
Financial Sector
Regulatory Factors: Controlling costs while meeting financial regulations and security standards.
Example Scenarios: Cost estimation for trading platforms, risk management tools, and financial data analysis.
Retail and Online Shopping
Scalability Needs: Pricing for busy retail and e-commerce sites, especially during peak times and sales events.
Case Studies: Cost management examples for online shops, inventory systems, and customer data analysis.
Manufacturing and IoT
IoT Device Costs: Estimating expenses for IoT device connections, data collection, and analytics in manufacturing.
Production Optimization: Pricing examples for monitoring production lines, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management.
Education and Research
Learning Platforms: Cost estimation for e-learning systems, research databases, and tools for student collaboration.
Research Initiatives: Managing expenses for large research projects, simulations, and data analysis.
GCP MASTERS
Protecting Data
Security Guidelines: Ways to keep data safe while controlling cloud expenses, such as using encryption and setting access limits.
Cost Considerations: Calculating expenses for security services like Identity and Access Management (IAM) and data protection tools.
Compliance Needs
Grasping Compliance: Important compliance rules for different sectors and their effects on cost management.
Compliance Tools: Leveraging GCP tools and features to ensure compliance while reducing costs.
Financial Effects of Security Actions
Cost and Security Balance: Analysing the financial effects of adopting advanced security measures compared to basic ones.
Real-World Examples: Instances of companies that have successfully managed security expenses while staying compliant.
Planning Your Migration
Cost Evaluation: Analysing the expenses related to moving current workloads to GCP, such as data transfer and system adjustments.
Migration Approaches: Various methods for migration (lift-and-shift, replatforming, refactoring) and their financial effects.
Post-Migration Optimization
Cost Optimization: Strategies for reducing costs after migration, including adjusting resource sizes and fine-tuning.
Monitoring Tools: Utilising GCP tools to track expenses and performance after migration.
Case Studies
Successful Migrations: Examples of organisations that effectively controlled costs during and after their cloud transition.
Challenges and Solutions: Typical issues encountered during migration and ways to overcome them.

Cost Management through Automation
Automating Cost Control
Automation Tools: A look at GCP tools and other solutions that help automate cost management tasks.
Use Cases: Instances of automated cost-saving actions, like automatic scaling and shutting down resources on a schedule.
Implementing Automation
Setting Up Automation: A simple guide to setting up automated cost management with GCP’s built-in tools and APIs.
Best Practices: Suggestions for effective automation, such as monitoring and fine-tuning automated tasks.
Benefits and Challenges
Advantages of Automation: The perks of automating cost management, including improved efficiency and fewer mistakes.
Overcoming Challenges: Typical issues faced when implementing automation and ways to tackle them.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Cost Analysis Techniques
Using BigQuery for Cost Insights: Learn how to utilise BigQuery to examine and display cloud spending information.
Custom Reports: Develop tailored reports and dashboards to understand cost trends and behaviours.
Integrating Analytics Tools
Merging Data Sources: Combine GCP cost data with other sources for a thorough analysis.
Visualisation Tools: Employ tools like Google Data Studio to produce in-depth cost reports and insights.
Enhancing Reporting
Automated Reporting: Create automated reports to consistently monitor and assess cloud expenses.
Actionable Insights: Discover how to leverage analytics for smart decisions and better cloud spending management.
Managing Expenses for DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
Understanding DevOps Expenses
Main Elements: Recognizing the key expense elements for DevOps pipelines, such as build environments, deployment methods, and monitoring tools.
Expense Estimation: Calculating costs for common tools and services in DevOps, including CI/CD pipelines, artefact storage, and automated testing.
Improving CI/CD Pipelines
Budget-Friendly Pipelines: Techniques for enhancing CI/CD pipelines to lower expenses while keeping performance and reliability intact.
Example Cases: Cost evaluation for different pipeline configurations, like on-demand versus reserved build instances, and refining pipeline stages.
Integration with GCP Tools
Utilising GCP Resources: Making use of GCP resources like Cloud Build, Cloud Source Repositories, and Cloud Functions in DevOps pipelines and their cost effects.
Cost Management Tips: Effective strategies for overseeing and reducing costs related to DevOps and CI/CD activities.
Cost Management for Deployments Across Multiple Regions
Deployments in Multiple Regions
Understanding Costs in Multiple Regions: Estimating expenses for launching applications and services in various regions, including data transfer and network costs.
Reducing Costs in Multiple Regions: Tips for lowering expenses in multi-region setups, like choosing the best regions and improving data replication.
Global Scaling Approaches
Scaling Worldwide: Cost factors for expanding applications globally, including content delivery networks (CDNs) and global load balancing.
Configuration Examples: Real-life examples showing how to manage costs for global deployments and ensure high availability.
Tracking and Controlling Global Costs
Tools and Methods: Resources and methods for tracking and managing expenses in global deployments, including cost distribution and detailed reports.
Best Practices: Effective strategies for managing global cloud expenses and making sure resources are used efficiently across different regions.
Building a Cost-Conscious Cloud Culture
Promoting Cost Awareness
Creating Awareness: Strategies for promoting cloud cost awareness within your organisation, including training and communication.
Cost-Conscious Culture: Building a culture where all team members are aware of and actively manage cloud costs.
Training and Education
Providing Training: Offering training programs and resources to help employees understand cloud pricing and cost management.
Educational Resources: Recommended resources, courses, and certifications for deepening knowledge of cloud cost management.
Incentivizing Cost Savings
Rewarding Savings: Implementing incentive programs to reward teams and individuals who contribute to cost-saving measures.
Tracking Impact: Measuring and tracking the impact of cost-saving initiatives on overall cloud spending and operational efficiency.

Conclusion
To effectively manage cloud costs, it’s important to understand the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Pricing Calculator, whether you’re new or experienced. This guide covers GCP’s pricing details, from basic ideas to advanced cost management methods. Knowing how GCP charges—like pay-as-you-go, sustained use discounts, or committed use contracts—helps you make smart choices that fit your budget.
The GCP Pricing Calculator is a useful tool for modelling different scenarios, estimating costs, and improving your cloud spending. We provide step-by-step instructions and real-life examples to show how to use this tool for precise cost estimates, whether you’re dealing with computer instances, storage, or multi-cloud setups.
Good cost management means not just using the Pricing Calculator but also including it in a wider financial plan. This involves budgeting, forecasting, and using automation to control costs. Fostering a cost-aware culture in your organisation can lead to significant savings and better efficiency.
As cloud technology and pricing continue to change, it’s vital to stay updated and adjust your strategies. Regularly using the Pricing Calculator, along with advice from industry experts and real-life examples, will help you manage cloud costs effectively. This way, you can optimise your cloud resources, cut unnecessary costs, and reach your financial goals more efficiently.
FAQ'S
The GCP Pricing Calculator is a tool that allows users to estimate the cost of using Google Cloud services. It helps you model different configurations, services, and usage patterns to predict potential costs before you deploy resources.
You can access the GCP Pricing Calculator through the Google Cloud website. Simply navigate to the Pricing Calculator page from the Google Cloud Console or search for “GCP Pricing Calculator” in your web browser.
Yes, the GCP Pricing Calculator allows you to save your estimates and share them with others. You can export estimates as JSON or PDF files and share them with team members or stakeholders for review and collaboration.
The estimates provided by the GCP Pricing Calculator are based on current pricing information and your selected configurations. While they are generally accurate, actual costs may vary due to factors like usage patterns, discounts, and pricing changes.
The Pricing Calculator covers most GCP services, including Compute Engine, Cloud Storage, BigQuery, Kubernetes Engine, and more. However, for some specialised or newly launched services, you may need to refer to specific pricing documentation or contact GCP support.
To optimise costs, use the Pricing Calculator to model different configurations and scenarios. Consider using features like sustained use discounts, committed use contracts, and preemptible VMs to find cost-effective solutions for your needs.
No, there is no cost to use the GCP Pricing Calculator. It is a free tool provided by Google Cloud to help users estimate and manage their cloud expenses.
Yes, the Pricing Calculator allows you to estimate costs for multi-region deployments. You can select different regions and configure your services to see how multi-region setups impact overall costs.
Pricing information in the GCP Pricing Calculator is updated regularly to reflect the latest changes in Google Cloud pricing. However, it’s a good practice to check for any recent updates or changes on the official Google Cloud pricing page.
If you notice discrepancies between your estimates and actual costs, review your GCP billing details and compare them with your Pricing Calculator estimates. For persistent issues or clarifications, you can contact Google Cloud support for assistance.

